Draft it Help System
The complete Help system for Draft it is available on these pages.
Available in: FREE, Plus, Pro and Architectural
Click on this button
 create a linear array. This command is not available until a selection set
is present. i.e. you must pre-select the item(s) to array before selecting the array command.
create a linear array. This command is not available until a selection set
is present. i.e. you must pre-select the item(s) to array before selecting the array command.
Once you have selected the item(s) to array select the button and the prompt reads:
Give Reference Point:
Now select a reference point using any of the snaps and input options. This is the point by which the array offset distances are measured, any point/position can be used here but it makes sense to use one that has some relevance to the selected item(s).
The prompt now reads:
Give point to Array to:
The system toolbar changes to display the snaps and input options.
Similar to the following (depending upon the last use).

The Ribbon changes to display options for the array, 'No.' and 'Fit Copies'
as follows.
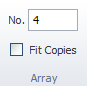
Each time the Draft it program is started the values for these fields to the defaults, subsequently they retain the values last used. These values are 'No.' the number of copies and 'Fit Copies'.
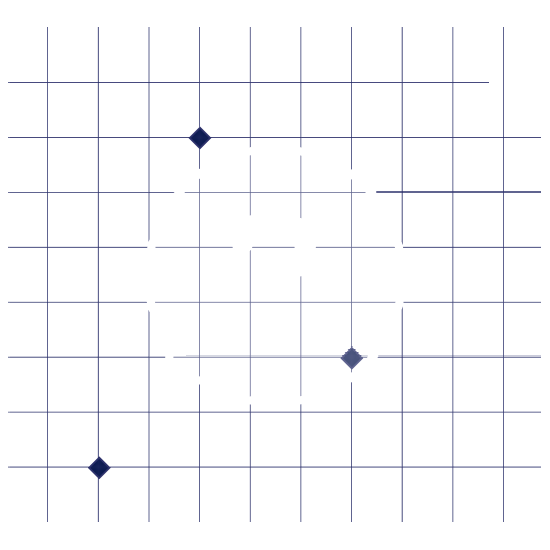
The spacing of the array copies is controlled by the distance from the 'Reference Point' to the cursor. A dynamic line is drawn between these positions and as the mouse is moved
multiple copies of the selection set will also move dynamically. The position of this 'point to array to'
can be specified using any of the snaps and input options.
Most commonly as it is a rectangular array the
 X, Y input option would be used to specify the distances between each copy in X & Y.
X, Y input option would be used to specify the distances between each copy in X & Y.
In the example below 'No.' is set to 2 and the spacing is defined as 50.
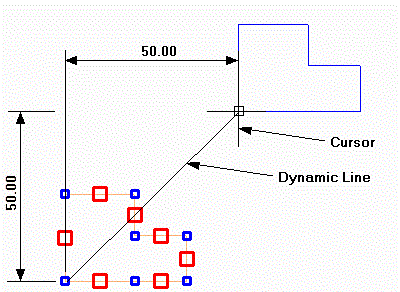
Let's look at the affect of the 'Fit Copies' option. This option changes how the spacing values are interpreted. If in the example above the No. was set to 5 then you can see that the 5 copies spaced with a gap of 50 in X and 50 in Y between each one. This is because the spacing defined is used as an incremental spacing. When 'Fit Copies' is selected the spacing becomes the total absolute span of the array.
Here is another example to demonstrate.
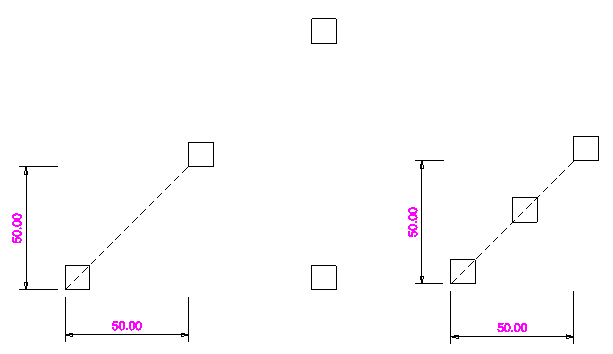
This example is a 10mm square with 3 copies.
On the left the spacing in 50 in X and in Y, as represented by the dotted line. On the right all of the values are identical but 'Fit Copies' is selected, so the copies are equally spaced between the distances or 2 points.